Clinical Studies
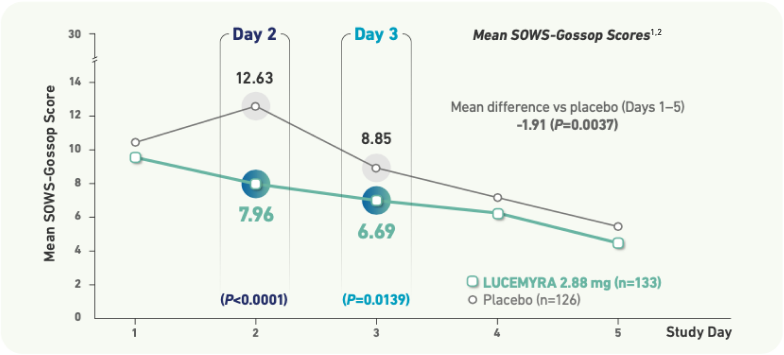
In a 5-Day treatment study, LUCEMYRA® significantly reduced the severity of withdrawal symptoms
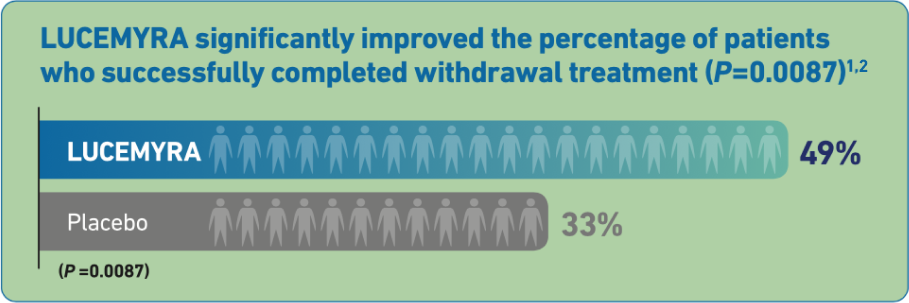
5-Day study design1.2 US-based, phase 3, randomized, multicenter, double- blind, placebo-controlled study involving patients (N=264) who were dependent on opioids (based on DSM-IVTM criteria). The study utilized a parallel-group design that consisted of two main phases conducted over an 8-day period: a 5-day treatment phase and a 2-day post-treatment phase. During the 5-day treatment phase, one cohort received LUCEMYRA 2.88 mg total daily (0.72 mg four times daily), while the other cohort received a matching placebo dose four times daily. All patients received four placebo tablets QID on Days 6 and 7. On Day 8, patients did not receive medication and were discharged after completing the required assessments. Efficacy and safety were also assessed on Days 6-7. Clinical endpoints included mean SOWS-Gossop total score on Days 1 through 5 of treatment, and proportion of patients who completed 5 days of treatment.
Patients receiving LUCEMYRA were significantly more likely to stay in treatment, as compared with placebo (P-0.0034)2
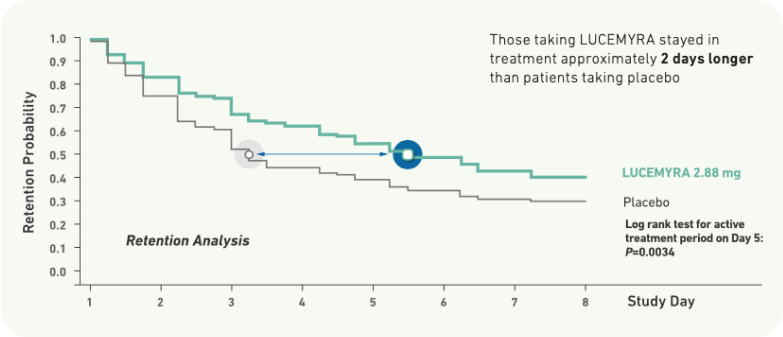
Those taking LUCEMYRA stayed in treatment approximately 2 days longer than patients taking placebo
Short Opiate Withdrawal Scale of Gossop (SOWS-Gossop) is a subject rated instrument that measures symptoms’ severity3
- Reductions in SOWS-GOSSOP scores indicate alleviation of opioid withdrawal symptoms
- Score differences of approximately 2-4 points represent a clinically meaningful improvement on SOWS-Gossop assessment
- LUCEMYRA® (lofexidine) [Prescribing Information]. USWM, LLC; 2020
- Data on file. US WorldMeds; 2017. 7. (ASAM). National practice guideline for the treatment of opioid use disorder: 2020 focused update. 2020. https://www.asam.org/Quality-Science/quality/2020 -national-practice-guideline. Accessed July 13, 2020.
- Vernon MK, Reinders S, Mannix S, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the 10-item Short Opiate Withdrawal Scale-Gossop (SOWS-Gossop) in patients undergoing opioid etoxification. Addict Behav. 2016;60:109-116.



